 EUIPO entirely rejected opposition No. 3 094 752 against all the goods of European Union trade mark application No 18 039 001 (figurative). Its proprietor Izvor Relax EOOD is represented by the team of IPConsulting Ltd. The opposition is based on two trademarks – European Union trade mark registration No 9 407 123 and French trade mark registrations No 3 460 479 and No 96 621 529, all for the word mark ‘OPTICLAIR’.
EUIPO entirely rejected opposition No. 3 094 752 against all the goods of European Union trade mark application No 18 039 001 (figurative). Its proprietor Izvor Relax EOOD is represented by the team of IPConsulting Ltd. The opposition is based on two trademarks – European Union trade mark registration No 9 407 123 and French trade mark registrations No 3 460 479 and No 96 621 529, all for the word mark ‘OPTICLAIR’.
Likelihood of confusion — article 8(1)(b) EUTMR
Whether a likelihood of confusion exists depends on the appreciation in a global assessment of several factors, which are interdependent. These factors include similarity of the signs, similarity of the goods and services, distinctiveness of the earlier mark, distinctive and dominant elements of the conflicting signs, and the relevant public.
The goods
The goods are directed at the public at large and business customers with specific professional knowledge or expertise. The degree of attention will be high in relation to some of the contested goods which are of a specialised nature and may have an impact on the health of the eyes.
Signs of the conflicting trademarks
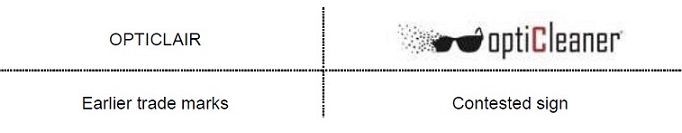
Visually – while it is true that the signs coincide in the letters ‘OPTICL, they cannot, for that reason alone, be regarded as visually similar. Indeed, it is to be taken into account that the initial letters OPTI(C) form a non-distinctive prefix. In view of this and the fact that the signs differ in their remaining letters, except for their common final R, the signs are visually similar to a low degree.
Aurally – number of syllables is different and so is their rhythm and intonation. Therefore, the signs are aurally similar to a low degree.
Conceptually – although the coinciding component ‘OPTI(C)’ will evoke a concept, it is not sufficient to establish any relevant conceptual similarity, as, this element is non-distinctive and cannot indicate the commercial origin of the goods at issue.
Conclusion of EUIPO Opposition division
The conceptual differences as regards at least part of the relevant public, are sufficient to immediately counteract the low visual and phonetic similarity between the signs. As to the remaining part of the public for which a conceptual comparison is not possible, it is considered that the differences between the signs are clearly perceptible and sufficient to exclude any likelihood of confusion between the marks.
Therefore, the opposition is not well founded under Article 8(1) EUTMR and must be rejected.
