 Florian is a family-based firm, established in Ruse, Bulgaria in 1999. They are a market-leader in the field of agriculture, supplying the needs both of professional and amateur horticulturists.
Florian is a family-based firm, established in Ruse, Bulgaria in 1999. They are a market-leader in the field of agriculture, supplying the needs both of professional and amateur horticulturists.
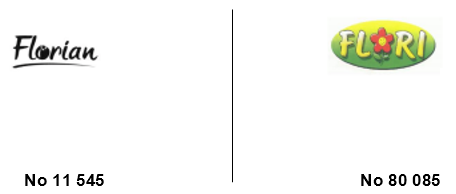
Florian, represented by IP Consulting, filed an opposition against all the goods and services of European Union trademark application No 15 800 824 for the word mark “Floris”. The opposition is based on European Union trademark reg. No 11 545 472, a figurative mark, and Bulgarian trade mark reg. No 80 085, a figurative mark, both shown below:
The opponent invoked Article 8(1)(b) EUTMR, which concerns likelihood of confusion. Likelihood of confusion exists where there is a risk the public to believe that the goods or services in question come from the same undertaking or from an economically linked undertaking. In order to determine if such likelihood exists, an assessment of several interdependent factors needs to be done.
“These factors include the similarity of signs, the similarity of the goods and services, the distinctiveness of the earlier trademark, the distinctive and dominant elements of the conflicting signs, and the relevant public.”
In comparison with the Bulgarian trade mark, the goods for which both trade marks are registered may coincide in their purpose, relevant public, origin and distribution, mainly in Class 1 of the opposition’s trade mark and Class 35 of the applicant’s. Furthermore, when a sign consists of both verbal and figurative components, the verbal component of the sign usually has a stronger impact on the consumer than the figurative one. The signs are aurally highly similar as they are of similar length and vowel structure. As their distinctiveness happens to be at the end of the sign, it catches the attention of the reader less. The flower in No 80 085 is not of significant importance, because the public’s attention to detail is perceived as average.
The EUIPO concludes that there is a likelihood of confusion on part of the public. The applicant’s trade mark is rejected for the goods found to be identical or similar to those of the earlier trade mark – the ones of Class 35.

